- Home
- About Us
- Book Appointment
- Treatments
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Anti-Aging
- Autism
- Autoimmune Disorders
- Back Pain
- COPD
- Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis
- Erectile dysfunction and Penis enlargement
- Fibromyalgia
- Hip Pain
- Knee Pain
- Lupus
- Lyme Disease
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Muscular dystrophy
- Parkinsons Disease
- Peripheral And Diabetic Neuropathy
- Post Cancer Treatments
- Post Stroke Recovery
- Psoriasis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Shoulder Pain
- Join The Club
- Aesthetics
- Blog
- Contact Us
Stem cell therapy is a breakthrough in the medical space, offering hope to millions of people worldwide. The utilization of stem cells for regenerative medicine extends beyond the treatment of various health conditions. Cellular therapies are now used for post-cancer recovery and the reduction of cancer-related infection risks. Researchers are studying new ways of using stem cells to fight cancer and help survivors recover faster.
This blog post will cover stem cells, the types of cells used, what they treat, how the therapy works, and the benefits of stem cell treatment in cancer recovery.
Table of Contents:
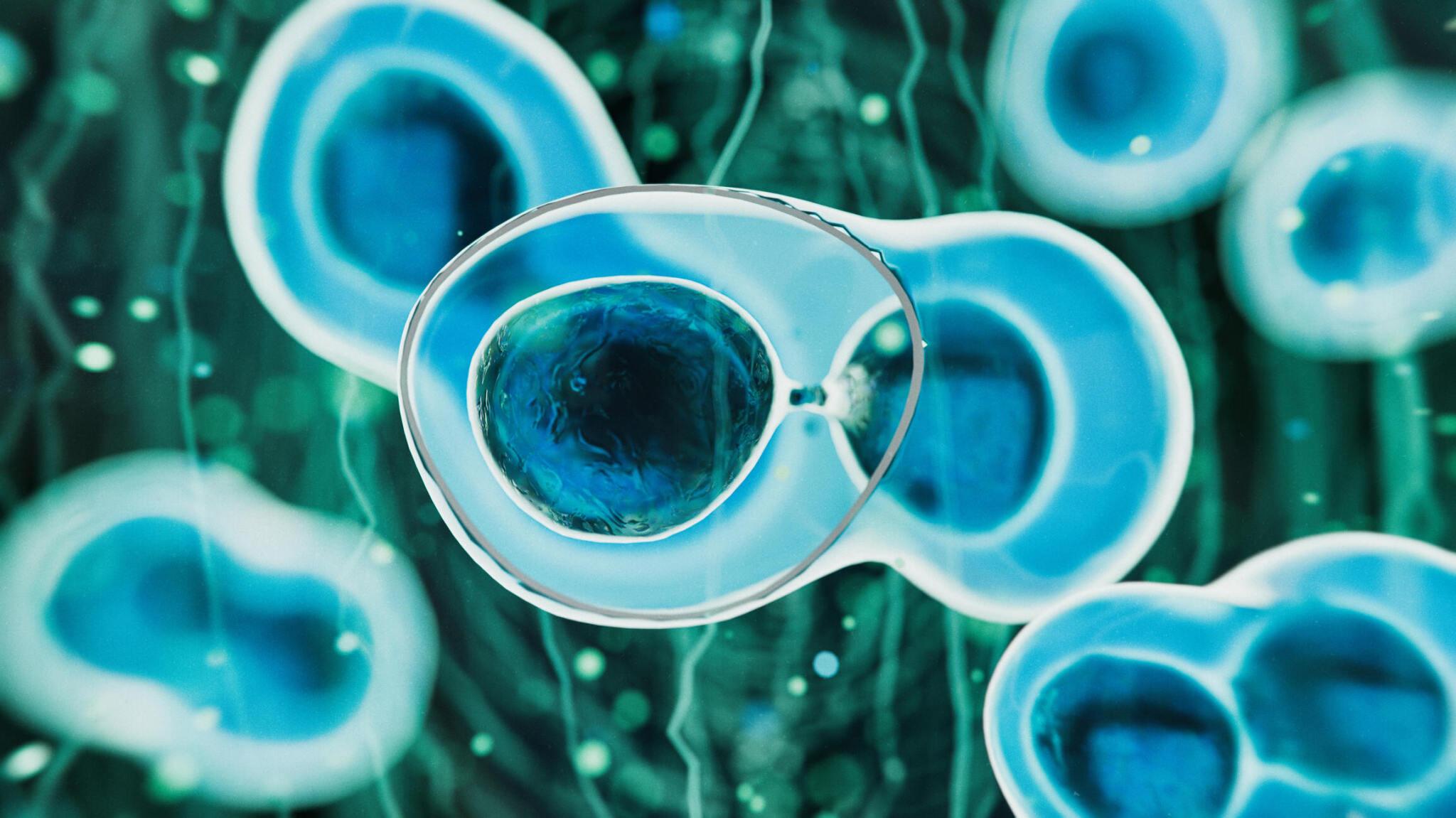
Introduction to Stem Cells
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells present in every human body, capable of forming cells of any type. In certain cases, they can even replicate themselves and renew cells an infinite number of times. This remarkable differentiation potential of stem cells makes them ideal candidates for treating chronic conditions, including post-cancer recovery.
Stem cells, for regenerative medicine, are collected from adult tissues (bone marrow or adipose tissue), embryos, or human umbilical cord tissues. Based on their sources and differentiation capabilities, they are classified as somatic stem cells and pluripotent stem cells.
Somatic stem cells are adult cells present in tissues and organs of the human body. These cells can form cells of specific tissue or organs, and hence, their applications are limited. Embryonic stem cells and umbilical cord tissue-derived stem cells are pluripotent stem cells, meaning they can reproduce and regenerate into cell types.
Read Also: Healing Power Of Stem Cell Therapy: A Comprehensive Guide
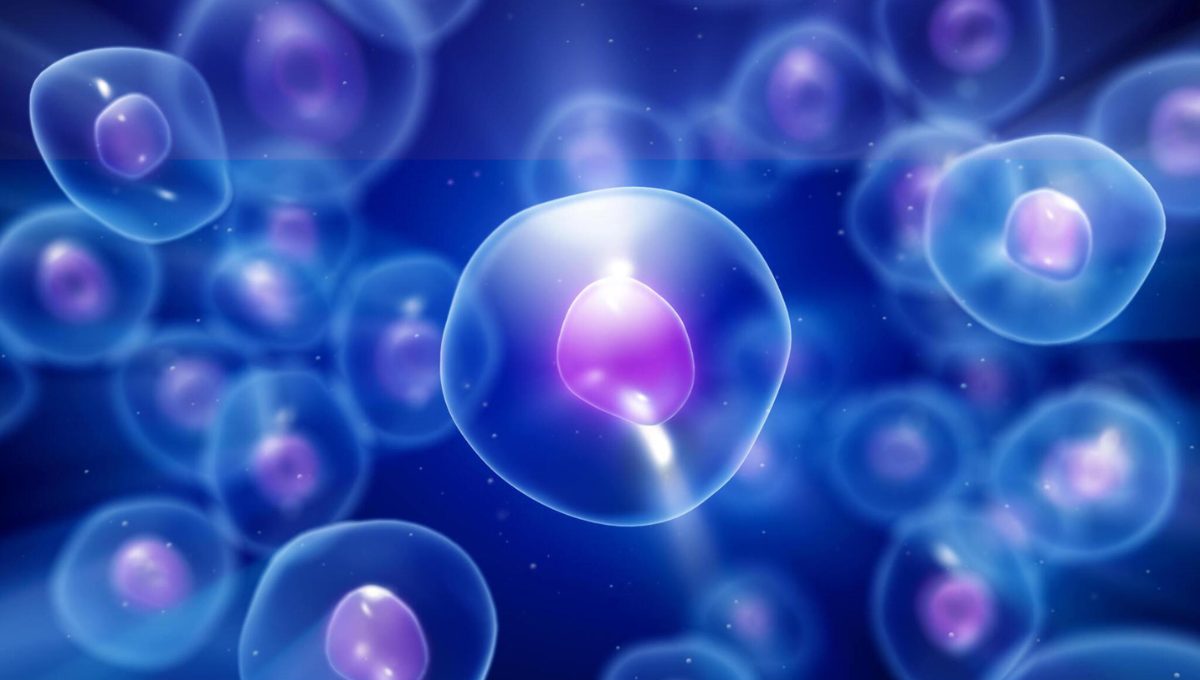
Types of Stem Cells Used in Cancer Treatment
A study by the National Library of Medicine suggests that three types of stem cells are used for cancer treatment. These types are from varied sources, exhibiting different proliferation, therapeutic, and differential potentials. Their properties determine their applications in post-cancer recovery.
Pluripotent Stem Cells (PSCs): Stem cells isolated from the inner mass cells of embryos or blastocysts that are in the early stage (3-5 days old) are pluripotent stem cells. Another source of PSCs is the umbilical cord tissue of Wharton’s Jelly collected after healthy and normal births.
Adult Stem Cells (ASCs): Mesenchymal stem cells fall under this group and can proliferate into specialized cell types, such as tissue or organs. These cells have unique biological characteristics to self-renew and generate tissue. By introducing therapeutic agents to the body, MSCs support cell therapies to reduce the side effects of cancer.
Cancer Stem Cells: These cells are immature progenitors of tumor cells produced by normal stem cell mutation. They are present in tumor tissues, and hence, targeting CSCs is a promising approach to treating solid cancerous tumors.
Conditions Stem Cell Therapy Can Treat
Although newer treatments and research are still ongoing, stem cells have proven to be effective in reducing the risks of infection in people with blood cancers. Cell-based therapy is used to heal the body from the inside after cancers that affect the body’s immune system and blood.
Conditions for which stem cell therapy is used to speed up the recovery process are –
- Leukemia – Blood cancer characterized by rapid growth of abnormal white blood cells.
- Neuroblastoma – Cancer that develops from immature nerve cells and mostly affects the adrenal glands.
- Lymphoma – A cancer of the lymphatic system involving lymphocytes, a type of white blood cells.
- Multiple Myeloma – A cancer of plasma cells in the bone marrow, causing rapid production of abnormal plasma cells.
How Stem Cells Aid In Post-cancer Healing
In simple terms, the introduction of stem cells replaces the damaged or cancerous cells and renews healthy cells to aid in the recovery of cancer patients.
The goal of stem cell therapy for cancer survivors is to stop the growth of cancerous cells to allow patients to live symptom-free lives and extend their lifespans. Stem cells can be introduced at various stages of the cancer, depending on the severity, patient’s age, and physical condition after the primary treatment.
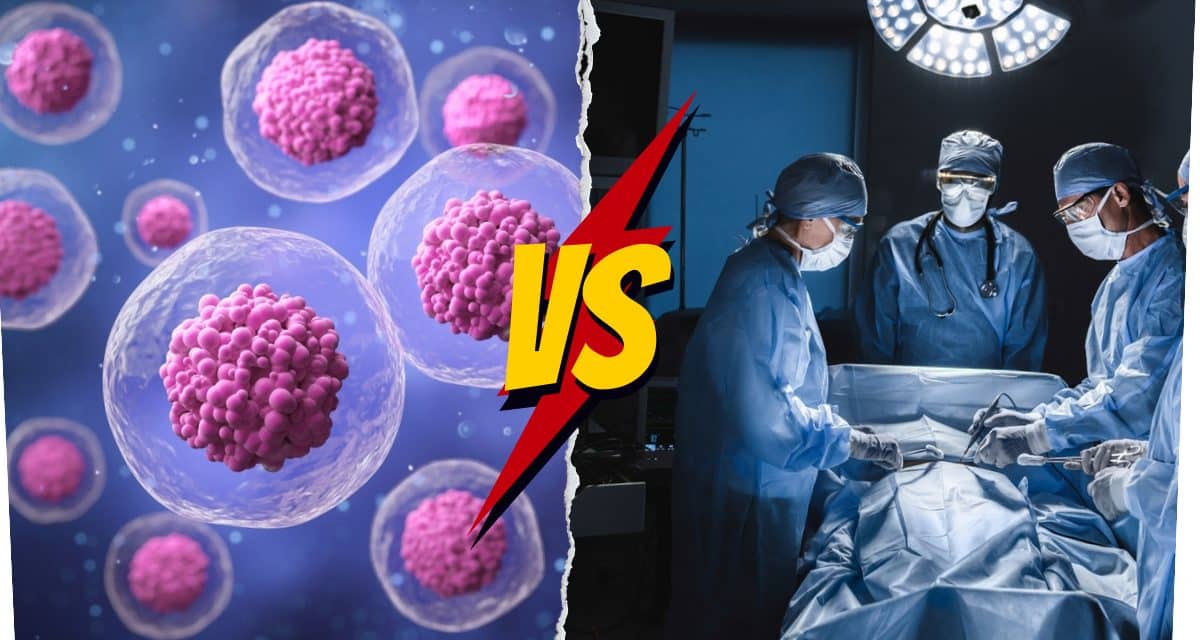
The primary treatment aims to eliminate cancer cells from the body by killing them or removing them. It can be surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, hormone therapy, or a combination of two or more of these.
Stem cells are typically used in the next two stages: adjuvant treatment and palliative treatment. After the patient receives the primary treatment, adjuvant therapy kills all those harmful cells that may cause cancer to recur or relapse. Palliative treatments are used to provide relief to patients from the side effects of the cancer.
Researchers believe that stem cells can prevent the uncontrollable growth of cancer cells. They use the concept of differentiation therapy, where newly introduced stem cells are forced to differentiate and replicate into mature and noncancerous cells. These cells stimulate the growth factors and cytokines (a protein vital for cell communication) and support the renewal of normal cells.
Read Also: Stem Cell Therapy: Ischemic Stroke Recovery Breakthrough
What You Can Expect After Treatment
Quality stem cell therapy helps patients cope better with the prolonged effects of cancer. It aims to give you a pain-free life free from cancer-related symptoms.
When you approach a stem cell therapy clinic, their medical team will examine your condition and evaluate your health history to plan a personalized treatment protocol for your condition.
Most patients receiving stem cells reported noticeable improvements, which enhanced their quality of life. From overall health conditions to increased appetite and better immunity to improvement in emotional health, cancer survivors can expect these changes, allowing them to lead a normal life.
Future of Regenerative Medicine
Since stem cell therapy is an emerging treatment approach, most people are skeptical about its efficacy. However, numerous studies and clinical trials demonstrate the therapeutic benefits of stem cells to address the long-term effects of cancer.
After decades of medical research and studies, clinicians are looking into the potential of stem cells for the treatment of autoimmune diseases, arthritis pain, signs of aging, and neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, etc.
Researchers are constantly working to find out other potentials of stem cells for future medicinal applications. Patients suffering from serious conditions or diseases are hopeful as more research and trials are ongoing.
Wrapping Up
It might seem unbelievable, but stem cells can do wonders by slowing down or preventing the progression of cancer. The introduction of stem cells through therapy aids in the faster recovery of the overall health of cancer fighters.
Traditional cancer treatments kill cancer cells, but there are chances of recurrence of the cancer. Cell-based therapy can lower the possibility of relapses, as it aims to replace the potential cancer cells with healthy cells, addressing the root cause of the cancer.
Stem cell treatments hold numerous advantages and open new approaches to post-cancer recuperation. With more research and trials, cellular therapy might become a part of standard treatment for various cancer types.
Want to learn more? Get a consultation with Dr. Josemaria Torres Farber of Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute, a leading stem cell clinic in Mexico, to gain insights on using stem cells for post-cancer treatment.