Benefits of Revolutionary Stem Cell Therapy To Treat Ischemic Stroke
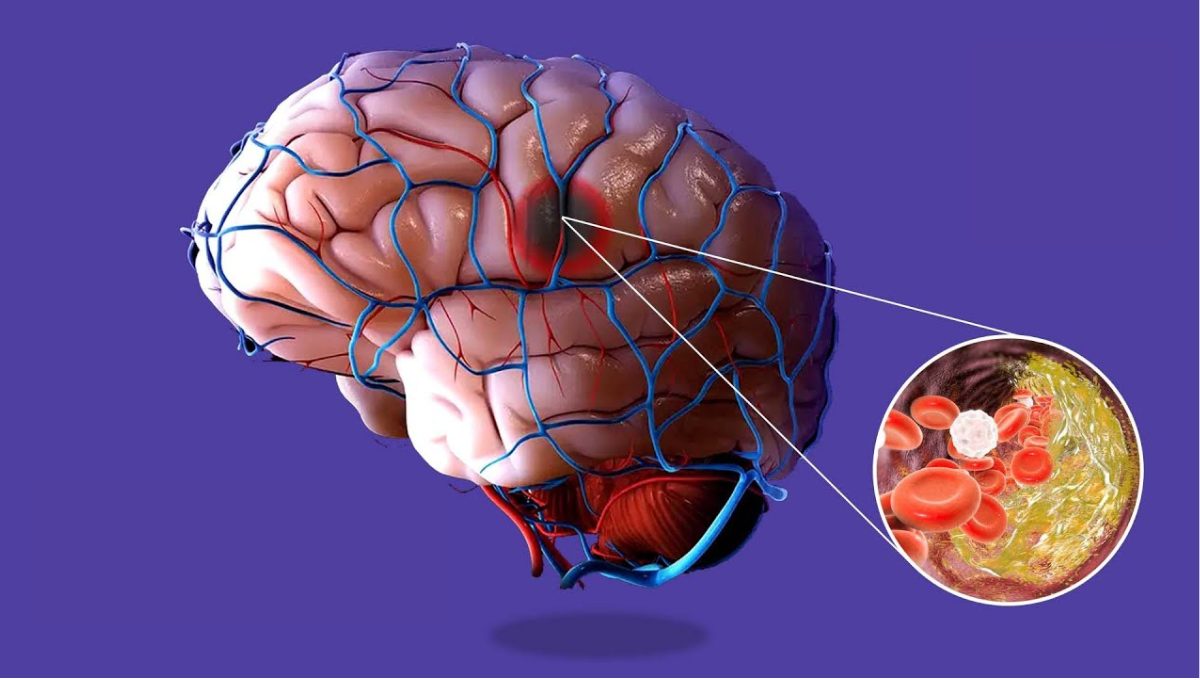
Stem cell therapy for post-stroke survivors helps improve cell replacement and enhances the neuroprotective abilities of the patient. 15 million stroke cases are reported by the World Health Organization annually. There are more than 80 million stroke survivors, out of which 70% of patients experienced ischemic stroke. Magnetic resonance angiography and brain CT scan can successfully detect a stroke attack. Mesenchymal stem cells play a pivotal role in regulating the immune system of patients who undergo this deadly cerebrovascular condition, ischemic stroke.
What are the Causes of Ischemic Stroke?
Ischemic stroke causes excitotoxic cell death, apoptosis, necrosis, and autophagy. Oxygen and blood supply to the brain are stopped when a patient experiences a stroke. Naturally, the brain is unable to process feelings and information. Blood clots in the artery and plaque in the blood vessels of the brain are the primary causes of ischemic stroke. Stenosis is another cause of this type of stroke due to the reduction of the artery passage. Transient ischemic attacks are the preliminary signs of conceiving a stroke. This entails the possibility of a bigger stroke attack.
Numbness, stiffness, confusion, and headaches that you experience suddenly and without any significant reasons are signs of ischemic stroke. However, these signs are non-conclusive. Nevertheless, speech difficulty, walking problems, and vision impairment are serious signs that a patient may experience a stroke. Physical, mental, and cognitive weaknesses are common problems experienced by stroke survivors. History of cardiac arrests, hypertension, high levels of cholesterol, sickle cell disease, birth control pills, drug abuse, and obesity are several factors that can cause a stroke.
[Read more: Know more Stem Cell Therapy In Atlanta]
What are Advanced Stem Cell Solutions for Stroke Patients?
Stroke rehabilitation stem cell treatment has significantly improved the living conditions of stroke survivors. Here are the 5 steps to provide regenerative medicine to stroke survivors –
Stem Cell Therapy Administration Eligibility
It is paramount to consider and evaluate several eligibility factors for a stroke patient before stem cell therapy is administered. The age, type of stroke, stroke severity, affected area of the brain, and the type of stem cells considered for the treatment plan are vital factors to certify a candidate for stem cell therapy.
Mode of Stem Cell Administration
Location-specific targeting for stem cell administration and intravenous (IV) infusions of stem cells are the best techniques to cure patients in the post-stroke recovery state. In most cases, experts create a customized plan for each individual who seeks stem cell treatment. The stem cells are introduced within the body through the veins that accelerate the regeneration abilities of the affected brain tissues.
Administration Protocol Compliance
Biomedical protocols are followed for safe stem cell therapy administration. Experts assess your condition, symptoms, and other criteria for a precise administration process.
Follow-Up on Treatment and Recovery
The results vary for each individual, and predicting the patient’s response time to the treatment is difficult. So, checking with the patients after periodic intervals is critical to determine their response to the stem cell treatment. Both patients and medical coordinators may have unresolved queries. The follow-up sessions help to address and resolve these issues for peace of mind and assurance. The total time for full recovery from the stroke attack after the stem cell therapy treatment is unprecedented. Following up with patients helps to identify if their brain functioning is enhanced. Also, it prevents the chance of future stroke attacks.
[Read more: Regenerative Medicine: What Are the Best Stem Cell Therapy Practices?]
What are the Benefits of Stem Cell Interventions in Stroke Recovery Treatment?
Ischemic stroke survivors experience rapid therapeutic benefits with the help of stem cell therapy during post-stroke treatment. Let us guide you through some noteworthy benefits of choosing this neurogenic therapy for stroke recovery –
- Revival of Neuron – Stimulate neuron regeneration in the brain with the help of human umbilical cord tissue-derived (Wharton’s Jelly) mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to regulate blood and oxygen circulation within the stroke-affected region of the brain.
- Tissue Regeneration – Stem cell therapy accelerates the production of tiny protein molecules known as chemokines in the ischemic areas, significantly repairing and regenerating the tissues in the affected brain region.
- Neurogenesis – Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) promote repairing and replacing damaged neurons with new healthy ones to improve and reverse the effects of ischemic stroke. This technique is known as neurogenesis.
- Revitalization of Blood Vessels – Ischemic tissues in the brain are damaged during a stroke due to plaque or blockades in the arteries. Stem cell therapy stimulates the formulation of new blood vessels within the affected brain areas to restore healthy mental and physical abilities.
- Active Immunomodulators – Stem cells are natural immunomodulators that enhance the abilities of your immune system for improved response to numerous conditions. In this case, they help to replace and repair damaged brain cells that are affected due to the stroke.
Additionally, stem cell therapy for stroke recovery offers more benefits such as stamina, energy, and muscle strength improvement, enhanced balance, mobility, and coordination, improved flexibility and strengthening of the joints, vision enhancement, attention and memory improvement, refined speech and facial movement, and independence of eating and swallowing.
Takeaway
Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute is a trustworthy clinic in Mazatlán, Mexico, offering swift stroke recovery solutions with holistic stem cell applications.
Therapeutic experts at LASCTI have more than 19 years of experience in treating stroke patients with pertinent stem cell therapy techniques. Explore and understand the diagnosis, processes, benefits, results, and promises we offer during and after your treatment for improved health and lifestyle.
Live an independent and healthy life with replenished repairing abilities and recover quicker if you experience a stroke attack. Uncover the monumental potential of MSCs with our carefully assessed treatment plan.

Regenerative Medicine: What Are the Best Stem Cell Therapy Practices?
Regenerative medicine focuses on the root causes of diseases, applying biological and engineering techniques to formulate distinct therapies to treat various illnesses.
Similarly, stem cell therapy is an emerging regenerative treatment solution for patients with numerous diseases. This type of therapy not only heals the damaged cells but also improves the immunomodulatory properties to fight complex diseases better.
You will be surprised to know that there are no concrete solutions or vaccines for chronic diseases such as HIV and malaria. Diabetes, osteoporosis, joint pain, and Alzheimer’s disease constantly make you suffer from pain. While doctors can only manage the symptoms, there is a ray of hope when these illnesses are treated through regenerative medicine and stem cell therapy.
Table of Contents
- What is Regenerative Medicine?
- What is Stem Cell Therapy?
- What are the Different Types of Stem Cells?
- What are the Applications of Stem Cell Therapy in Regenerative Medicine?
- Stem Cell Therapy Benefits in Regenerative Medicine
- Types of Diseases Treated at the Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute
What is Regenerative Medicine?
Regenerative medicine is the procedure to treat diseases that are caused due to damaged organs, cell depletion, and lost tissue. This treatment helps to replace and regenerate tissues utilizing the power of stem cell therapy. Activate the body’s natural healing abilities with this medicinal approach that detects and fixes chronic disorders. The end goal is to ensure a better life and health quality for patients who undergo chronic disease. Research is currently underway on regeneration medicine’s ability to treat heart conditions, diabetes, vision disorders, muscles, etc. Common regenerative medicine techniques are –
- 3D Organ Printing
- Organoids
- Tissue Engineering
What is Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cell therapy activates the body’s regenerative abilities to replenish damaged tissues and cells, fix the immune system, and prevent inflammatory conditions. While there are several different types of stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from the human umbilical cord tissues or Wharton’s Jelly are prevalently used to promote cellular healing techniques to improve the overall quality of your health. Cell death causes degenerative diseases and organ damage. Loss of function, chronic pain, and hair loss are common symptoms of these diseases. Most organs in the body do not possess regenerative abilities. Stem cell therapy emphasizes the natural regeneration of organs. Furthermore, stem cell therapies can treat multiple health conditions such as Psoriasis, Lupus, Rheumatoid arthritis, Lyme, multiple sclerosis, Chron’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, autism, fibromyalgia, joint pain, etc.
Moreover, this regenerative therapy provides relief for patients who undergo post-cancer treatment. Also, it helps reverse the effects of aging and offers anti-aging solutions.
In the next section, we will further explore the different types of stem cells harnessed to promote healthy living conditions.
What are the Different Types of Stem Cells?
- Embryonic Stem Cells – Undifferentiated cells with self-renewal and cell distinguishing abilities.
- Bone Marrow Hematopoietic Stem Cells – These stem cells can reform all blood-forming lineages.
- Bone Marrow Stromal Stem Cells – These stem cells can rapidly divide and treat bones, ligaments, cartilage, and muscles.
- Multipotent Adult Progenitor Cells – These stem cells have limited cell differentiation abilities.
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells – MSCs are multipotent with self-renewal abilities and have great differentiation capabilities for numerous cell types.
- Neural Stem Cells – Self-renewable cells that can distinguish between the different types of brain cells.
- Pancreatic Stem Cells – Derived from the fetal pancreas of the human body, PSCs are multipotent cells.
- Skin Stem Cells – This promotes the production of neural and mesodermal cells.
- Cardiac Stem Cells – These stem cells are present in the adult heart of human beings and repair the cells within the heart.
- Fat Stem Cells – Also known as Adipose Derived Stem Cells, they are an amazing source of regenerative medicine for an extended period.
- Olfactory Stem Cells – These are types of adult stem cells that can restore the natural healing abilities of the mucous membranes.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells – PSCs can detect the types of specialized cells throughout the different layers of the germ.
- Totipotent Stem Cells – These stem cells can distinguish between different types of cells within the human body.
- Unipotent Stem Cells – USCs can generate only one type of cell found in adult tissues. While it can constantly recreate cell populations, its treatment mode is limited due to reduced differentiation abilities.
[ Read Also: Know More About Stem Cell Therapy in Miami ]
What are the Applications of Stem Cell Therapy in Regenerative Medicine?
Mesenchymal stem cells have dynamic applications in the field of regenerative medicine. Let us examine how stem cell therapy promotes healthy living –
- Muscle degeneration disease treatment with active regeneration.
- Healing orthopedic conditions such as ligament, bone tissue, and cartilage regeneration.
- Regenerates bladder tissue to treat liver failure.
- Reconstitutes hair for normal growth, reversing the signs of hair loss.
- Post cardiac arrest treatment of the heart.
- Reverses the effects of spinal cord injury.
- Treatment for autoimmune diseases.
- Promotes the formation of insulin-secreting cells.
- Treats post-cancer and brain injury conditions.
- Regenerates teeth and ear repair.
Stem Cell Therapy Benefits in Regenerative Medicine
The regenerative abilities of stem cells restore the body’s healing abilities and kill pain-inducing factors in the long run. Let us explore the benefits –
- Effective pain reduction
- Minimum time for recovery post-recovery
- Improves bodily and organ functions and enhances regeneration abilities
- Avoid the risks and costs of surgeries
- Minimally invasive – administered via IV, IA, or IM techniques
[ Read Also: Stem Cell Treatment or Knee Replacement Surgery: A Comprehensive Guide]
Types of Diseases Treated at the Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute
Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute in Mexico is an American-owned and operated clinic with affordable stem cell therapy solutions for various diseases. Let us walk you through some of the diseases we treat –
- Autoimmune diseases – Alzheimer’s disease, Lyme, Lupus, multiple sclerosis, autism, fibromyalgia, psoriasis, and rheumatoid arthritis, are some autoimmune disorders treated with stem cell therapy and regenerative medicine.
- Cardiovascular diseases – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and post-stroke recovery are cured with the help of stem cell therapy.
- Gastrointestinal disorders – Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are treatable with stem cell therapy.
- Neurological disorders – Spinal cord injury, Parkinson’s disease, and peripheral and diabetic neuropathy are treated with stem cell therapy.
Bottomline
The cost of stem cell therapy in Mexico is economical compared to treatment facilities in the USA. Reputed and trusted experts from LASCTI have hands-on experience in treating different health conditions with regenerative stem cell therapy. Additionally, we offer medical tourism services, including pick-up and drop-off at our facility in Mazatlán. We ensure safe administration protocols and follow standard safety obligations. Join hands to explore stem cell therapies and regenerative medicine’s transformative power to improve overall health.
Stem Cell Therapy: A Revolutionary Alternative to Invasive Surgery
Stem cell therapy has emerged as a groundbreaking alternative to traditional invasive surgeries. By harnessing the body’s natural healing capabilities, this innovative treatment offers numerous benefits, including reduced recovery times, minimized risks, and enhanced outcomes. The Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute, an American-owned and operated facility, is at the forefront of this medical revolution, utilizing mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from Wharton’s Jelly in the umbilical cord. This article explores how stem cells are used instead of invasive surgery, the follow-up process, and the outcomes associated with this advanced treatment.
The Promise of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy represents a paradigm shift in medical treatment. Unlike traditional surgeries, which often involve significant incisions, prolonged recovery periods, and potential complications, stem cell therapy is minimally invasive. The treatment involves the administration of stem cells to damaged tissues, where they stimulate repair and regeneration. This approach not only reduces the need for extensive surgical procedures but also promotes faster healing and improved overall health.
[Read more: Transforming Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment with Stem Cell Therapy]
How Stem Cells Work
Stem cells are unique in their ability to differentiate into various cell types, making them ideal for repairing damaged tissues. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), particularly those derived from Wharton’s Jelly in the umbilical cord, are known for their regenerative properties. These cells can transform into bone, cartilage, muscle, and other tissue types, making them highly versatile in medical applications.
Applications of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy has a wide range of applications, effectively treating conditions that traditionally required invasive surgeries. Some of the key areas include:
- Orthopedic Conditions: Stem cell therapy is highly effective in treating joint injuries, osteoarthritis, and chronic pain. MSCs can regenerate cartilage and bone tissue, offering relief and improved mobility without the need for joint replacement surgery.
- Neurological Disorders: For conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and stroke recovery, stem cells provide hope by repairing neural damage and restoring function.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Stem cell therapy can aid in the regeneration of heart tissue after a heart attack, improving heart function and reducing the need for invasive cardiac procedures.
- Autoimmune Diseases: MSCs modulate the immune system, making them effective in treating autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Crohn’s disease.
- Cosmetic and Anti-Aging Treatments: Stem cell therapy is also gaining popularity for its anti-aging benefits, rejuvenating the skin and reducing the appearance of wrinkles and scars.
Procedure of Stem Cell Therapy
The procedure for stem cell therapy is straightforward and minimally invasive. It involves the following steps:
- Consultation and Evaluation: Patients undergo a thorough evaluation to determine their eligibility for stem cell therapy. This includes medical history, diagnostic tests, and imaging studies.
- Stem Cell Harvesting: At the Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute, MSCs are sourced from Wharton’s Jelly in the umbilical cord. This non-invasive method ensures a high yield of potent stem cells.
- Cell Preparation: The harvested stem cells are processed and prepared for administration. This step ensures that the cells are viable and ready to promote healing.
- Injection or Infusion: Depending on the condition being treated, stem cells are either injected directly into the affected area or administered through an intravenous infusion.
- Post-Treatment Care: Patients receive detailed post-treatment care instructions to optimize recovery and maximize the benefits of the therapy.
Follow-Up and Outcomes
Stem cell therapy is renowned for its positive outcomes and reduced recovery times compared to invasive surgeries. The follow-up process is critical to ensure the success of the treatment and involves several stages:
- Immediate Post-Treatment: Patients are monitored for a short period after the procedure to ensure there are no immediate adverse reactions. Most patients experience minimal discomfort and can resume normal activities within a few days.
- Short-Term Follow-Up: Over the next few weeks, patients typically attend follow-up appointments to assess the progress of healing. During these visits, doctors may use imaging studies to evaluate tissue regeneration and address any concerns.
- Long-Term Follow-Up: Long-term follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor the ongoing effects of the therapy. These visits help track the sustained benefits of the treatment and ensure that the patient maintains optimal health.
Success Rates and Patient Satisfaction
The success rates of stem cell therapy are highly encouraging. Studies have shown that patients experience significant improvements in pain relief, mobility, and overall quality of life. For example, a study published in the Journal of Clinical Orthopaedics and Trauma reported that 85% of patients with osteoarthritis experienced substantial pain relief and improved joint function following stem cell therapy.
Moreover, patient satisfaction is exceptionally high. Many individuals who have undergone stem cell therapy express gratitude for the minimal downtime and the ability to avoid the risks and complications associated with invasive surgeries. Testimonials from patients at the Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute highlight the life-changing benefits of this treatment.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy is transforming the landscape of modern medicine, offering a viable alternative to invasive surgeries. With its ability to harness the body’s natural healing mechanisms, this treatment provides numerous advantages, including reduced recovery times, fewer risks, and improved outcomes. The Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute, with its focus on using mesenchymal stem cells derived from Wharton’s Jelly, is leading the way in delivering these cutting-edge therapies.
As the medical community continues to explore the full potential of stem cells, the future looks promising. Patients suffering from a variety of conditions now have hope for a less invasive and more effective treatment option. Whether dealing with orthopedic injuries, neurological disorders, cardiovascular diseases, or autoimmune conditions, stem cell therapy offers a path to healing and improved health without the need for invasive surgery. The journey to better health starts with understanding the transformative power of stem cells and embracing this innovative approach to medicine.
The Power of Stem Cell Therapy: A Closer Look at Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Wharton’s Jelly
Stem cell therapy is revolutionizing the medical field, offering hope for conditions once deemed untreatable. This innovative approach harnesses the power of stem cells to repair, replace, and regenerate damaged tissues and organs. One of the most promising types of stem cells used in regenerative medicine is Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs), particularly those derived from Wharton’s Jelly. This blog will explore the science behind MSCs, the unique properties of Wharton’s Jelly-derived MSCs, their immunomodulatory effects, and their potential in treating pulmonary fibrosis. Additionally, we will delve into clinical trials, the landscape of stem cell therapy in Mexico, and its costs, providing a comprehensive overview of this groundbreaking therapy.
What are Mesenchymal Stem Cells?
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) are multipotent stem cells capable of differentiating into various cell types, including bone, cartilage, muscle, and fat cells. MSCs are prized for their ability to modulate immune responses, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue repair. These cells can be isolated from various tissues, including bone marrow, adipose tissue, and the umbilical cord.
Key Characteristics of MSCs
- Multipotency: Ability to differentiate into multiple cell types.
- Immunomodulation: Capable of modulating the immune system to reduce inflammation.
- Tissue Repair: Promote the repair and regeneration of damaged tissues.
- Homing Ability: Can migrate to sites of injury or inflammation.
What is Wharton’s Jelly?
Wharton’s Jelly is a gelatinous substance found within the umbilical cord. It surrounds the umbilical vein and arteries, providing protection and structural support. Wharton’s Jelly is rich in MSCs, which are easier to harvest and have higher proliferation rates compared to MSCs from other sources.
Unique Properties of Wharton’s Jelly
- Abundant MSCs: High concentration of MSCs, making it a potent source for regenerative therapies.
- Ethical Collection: Obtained non-invasively from donated umbilical cords post-birth.
- Young Cells: MSCs from Wharton’s Jelly are young and exhibit robust regenerative capabilities.
Wharton’s Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (WJ-MSCs)
Wharton’s Jelly-derived MSCs (WJ-MSCs) are gaining attention for their exceptional regenerative and immunomodulatory properties. These cells can be used to treat a variety of conditions, including pulmonary fibrosis, a severe lung disease characterized by scarring of lung tissue.
Benefits of WJ-MSCs
- High Proliferation Rate: Rapidly divide and expand in culture.
- Potent Immunomodulation: Strong ability to modulate the immune response.
- Non-invasive Collection: Obtained ethically without harming the donor.
Read Also: Advanced Cost-Effective Stem Cell Treatment for Miami Patients
Immunomodulatory Effects of Wharton’s Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
WJ-MSCs have remarkable immunomodulatory effects, which are crucial for treating autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. They can suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines and promote the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, thus reducing inflammation and preventing tissue damage.
Mechanisms of Immunomodulation
- Cytokine Secretion: Release of anti-inflammatory cytokines.
- T-Cell Modulation: Suppress the activity of pro-inflammatory T-cells.
- Macrophage Polarization: Promote the transition of macrophages to an anti-inflammatory phenotype.
Mechanism of Action of WJ-MSCs on Pulmonary Fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis involves the thickening and scarring of lung tissue, leading to severe respiratory issues. WJ-MSCs can potentially reverse this damage through several mechanisms:
How WJ-MSCs Help in Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Reduce lung inflammation, which is a primary cause of fibrosis.
- Anti-fibrotic Properties: Inhibit the processes that lead to scar tissue formation.
- Regenerative Capacity: Promote the repair and regeneration of damaged lung tissue.
Clinical Trials in the Field of Cell Therapy Using Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Pulmonary Fibrosis
Clinical trials are crucial in establishing the efficacy and safety of stem cell therapies. Several trials are underway to investigate the use of MSCs, including WJ-MSCs, in treating pulmonary fibrosis.
Key Findings from Clinical Trials
- Safety: WJ-MSCs have been shown to be safe with no serious adverse effects.
- Efficacy: Preliminary results indicate improvements in lung function and reduction in fibrosis markers.
Stem Cell Therapy: An Overview
Stem cell therapy involves the transplantation of stem cells to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs. It has shown promise in treating a variety of conditions, from neurological disorders to cardiovascular diseases.
Read Also: Unlocking the Potential of Stem Cells for Heart Failure and Stroke Recovery
Applications of Stem Cell Therapy
- Neurological Disorders: Treatment of stroke, spinal cord injuries, and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Repair of heart tissue post-myocardial infarction.
- Orthopedic Conditions: Treatment of joint and bone injuries.
Stem Cell Therapy in Mexico
Mexico has become a hub for stem cell therapy, attracting patients worldwide due to its advanced medical facilities and affordable treatment options. The country offers high-quality care with significantly lower costs compared to the United States and Europe.
Cost of Stem Cell Therapy in Mexico
- Affordability: Treatments in Mexico can be up to 70% cheaper than in the U.S.
- Quality of Care: Many clinics, such as Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute, are American-owned and operated, ensuring high standards of care.
Key Clinics in Mexico
- Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute: American-owned and operated, specializing in the use of Wharton’s Jelly-derived MSCs for various treatments.
Follow-up and Outcomes
Post-treatment follow-up is crucial to monitor the patient’s progress and ensure the success of stem cell therapy. Regular check-ups and assessments help track the efficacy of the treatment and manage any potential side effects.
Monitoring Progress
- Regular Assessments: Periodic evaluations to monitor improvement in symptoms.
- Patient Feedback: Collecting data on patient experiences and outcomes.
- Adjustments: Modifying treatment protocols based on individual responses.
Conclusion
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs), particularly those derived from Wharton’s Jelly, represent a promising frontier in regenerative medicine. Their unique properties make them ideal for treating a range of conditions, including pulmonary fibrosis. Clinical trials continue to validate their efficacy and safety, paving the way for broader applications. Stem cell therapy in Mexico offers an affordable and high-quality alternative for patients seeking advanced treatments. With ongoing research and clinical advancements, MSCs hold the potential to revolutionize medical care and improve the lives of countless individuals.
Stem Cell Therapy Implant Shows Promise For Type 1 Diabetes
The field of regenerative medicine has been buzzing with excitement due to recent advancements in stem cell therapy, particularly for treating chronic conditions like Type 1 Diabetes (T1D).
The potential of stem cells to revolutionize diabetes treatment represents a beacon of hope for millions worldwide. This blog delves into the groundbreaking developments, clinical successes, and future prospects of stem cell therapy for diabetes, especially focusing on Type 1 Diabetes.
Introduction
Stem cell therapy has long been heralded as a revolutionary approach to treating a myriad of diseases. The ability of stem cells to differentiate into various cell types makes them incredibly versatile and promising for regenerative medicine. For individuals with Type 1 Diabetes, the promise of stem cell therapy offers new hope for a life free from daily insulin injections and the constant monitoring of blood sugar levels. Recent advancements suggest that we are on the cusp of a major breakthrough in the treatment of this chronic condition.
Stem Cells for Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes is a condition in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This destruction leads to a lifelong dependency on insulin therapy to regulate blood sugar levels. Stem cells, particularly mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from Wharton’s Jelly in the umbilical cord, offer a potential solution. These MSCs have shown promise in differentiating into insulin-producing cells, potentially restoring the body’s ability to produce insulin naturally.
What Are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are unique cells with the ability to develop into different cell types in the body. They can divide and renew themselves over long periods, unlike other cells. There are various types of stem cells, including embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Each type holds potential for different therapeutic applications.
How Stem Cells Work for Diabetes
In the context of Type 1 Diabetes, stem cells can be guided to become insulin-producing beta cells. Once implanted into a patient, these cells could potentially take over the function of the destroyed pancreatic cells, producing insulin in response to blood glucose levels and thus managing the disease more effectively.
Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetes Success Rate
Stem cell therapy’s success rate for diabetes, while still under extensive research, shows encouraging signs. Various clinical trials and studies have demonstrated significant improvements in patients receiving stem cell therapy. For instance, in some studies, patients have shown increased insulin production and reduced insulin dependence after receiving stem cell transplants.
Clinical Trials and Success Stories
One of the notable clinical trials involved the transplantation of stem cell-derived beta cells into patients with Type 1 Diabetes. The results were promising, with several participants experiencing improved glycemic control and a reduction in the need for insulin therapy. These trials indicate a potential path forward for more widespread application of stem cell therapy in diabetes management.
Stem Cell Biology Suggests Promise as a Way to Treat Diabetes
The underlying biology of stem cells suggests a robust potential for treating diabetes. Stem cells’ ability to self-renew and differentiate into various cell types makes them ideal candidates for regenerating damaged tissues and organs.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are particularly promising due to their immunomodulatory properties and their ability to differentiate into various cell types, including insulin-producing cells. MSCs derived from Wharton’s Jelly in the umbilical cord are especially potent. These cells are less likely to cause an immune response and have shown great potential in preclinical and clinical studies for treating diabetes.
Clinical Trial Results for Type 1 Diabetes (T1D)
Clinical trials for stem cell therapy in Type 1 Diabetes have yielded promising results, showcasing the potential of this treatment to revolutionize diabetes management.
Notable Clinical Trials
Several clinical trials have examined the effectiveness of stem cell therapy in the treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. One such trial involved the infusion of autologous hematopoietic stem cells in newly diagnosed patients. The results showed that the majority of participants achieved insulin independence for an extended period post-treatment.
Another study focused on the use of mesenchymal stem cells derived from Wharton’s Jelly. Patients receiving these stem cells demonstrated significant improvements in glycemic control, reduced HbA1c levels, and increased C-peptide levels, indicating enhanced insulin production.
Statistical Success Rates
While still in the experimental stages, the success rates of these trials are promising. For example, in a clinical trial involving MSCs, over 60% of the participants experienced improved beta-cell function and reduced insulin requirements. These early results suggest that with further refinement, stem cell therapy could become a viable standard treatment for Type 1 Diabetes.
Why Use Mesenchymal Stem Cells?
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are favored for several reasons in the treatment of diabetes. Their unique properties make them ideal candidates for regenerative medicine.
Advantages of MSCs
- Immunomodulatory Properties: MSCs can modulate the immune system, reducing the autoimmune response that destroys pancreatic beta cells in Type 1 Diabetes.
- Differentiation Potential: MSCs can differentiate into insulin-producing beta cells, effectively replacing the destroyed cells in the pancreas.
- Ethical and Logistical Benefits: MSCs derived from Wharton’s Jelly in the umbilical cord are easily accessible and do not pose the ethical concerns associated with embryonic stem cells.
- Low Risk of Rejection: These cells are less likely to be rejected by the recipient’s immune system, making them safer for clinical use.
Current Stem Cell Research for Diabetes: Limitations
Despite the promise of stem cell therapy for diabetes, there are several limitations and challenges that researchers are currently addressing.
Technical and Biological Challenges
- Differentiation Efficiency: Ensuring that stem cells efficiently differentiate into functional insulin-producing cells remains a significant challenge.
- Longevity and Stability: The long-term stability and functionality of transplanted stem cells need to be thoroughly investigated to ensure lasting benefits.
- Safety Concerns: Potential risks, such as tumorigenesis and immune reactions, must be carefully managed and mitigated.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
The regulatory landscape for stem cell therapies is complex, with rigorous standards for safety and efficacy. Additionally, ethical considerations regarding the source of stem cells and the implications of genetic modifications play a crucial role in shaping research and clinical applications.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
While this blog focuses primarily on Type 1 Diabetes, understanding Type 2 Diabetes provides context for the broader impact of diabetes on global health.
Overview of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency. Unlike Type 1 Diabetes, where the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing cells, Type 2 Diabetes is often associated with lifestyle factors and genetics.
Differences Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
- Cause: Type 1 is autoimmune; Type 2 is primarily lifestyle-related.
- Onset: Type 1 diabetes usually develops in childhood or adolescence, while Type 2 diabetes typically occurs in adults.
- Management: Type 1 requires insulin therapy; Type 2 can often be managed with lifestyle changes and oral medications.
Is There a Cure for Diabetes?
Currently, there is no definitive cure for diabetes. However, advancements in medical research, including stem cell therapy, are paving the way for potential cures, especially for Type 1 Diabetes.
Potential for a Cure
Stem cell therapy offers the potential to regenerate insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, holding the promise of a cure. Clinical trials and ongoing research aim to achieve this goal, offering hope for a future where diabetes can be effectively cured.
Read Also: Advanced Stem Cell Therapy for New York Patients
Where Can I Get Stem Cell Treatment for Diabetes?
For those interested in exploring stem cell treatment for diabetes, several reputable institutions and clinics offer these services.
Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute
Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute, an American-owned and operated facility, is at the forefront of providing advanced stem cell treatments. They utilize mesenchymal stem cells derived from Wharton’s Jelly in the umbilical cord, offering cutting-edge therapy options for diabetes.
Other Reputable Clinics
Numerous other clinics worldwide specialize in stem cell therapy for diabetes. It is crucial to choose a clinic with a proven track record, experienced medical staff, and stringent safety protocols.
Can Stem Cells Treat Diabetes?
Stem cell therapy is emerging as a promising treatment option for diabetes, particularly Type 1 Diabetes.
Mechanism of Action
Stem cells can potentially treat diabetes by differentiating into insulin-producing cells and repairing the damaged pancreatic tissue. This approach aims to restore the body’s natural ability to produce and regulate insulin, thereby managing or even curing the disease.
Success Stories and Case Studies
Several case studies and patient testimonials highlight the success of stem cell therapy in improving glycemic control and reducing insulin dependence. These stories underscore the potential of stem cell therapy to transform the lives of those living with diabetes.
Follow-up and Outcomes
Post-treatment follow-up is crucial to monitor the outcomes and ensure the long-term success of stem cell therapy for diabetes.
Read Also: Transforming Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment with Stem Cell Therapy
Monitoring and Support
Patients undergoing stem cell therapy for diabetes require regular monitoring to assess the functionality of the transplanted cells and manage any potential complications. Continuous support and follow-up care are essential to optimize treatment outcomes and improve the quality of life.
Long-term Outcomes
While short-term results are promising, long-term studies are needed to confirm the durability and effectiveness of stem cell therapy for diabetes. Ongoing research aims to address these questions and provide comprehensive data on the long-term outcomes of this innovative treatment.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy represents a significant advancement in the treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. The ability of mesenchymal stem cells, particularly those derived from Wharton’s Jelly in the umbilical cord, to differentiate into insulin-producing cells offers a promising avenue for restoring pancreatic function and potentially curing the disease. While challenges remain, the progress in clinical trials and research highlights the transformative potential of stem cell therapy for diabetes. With continued innovation and rigorous scientific exploration, we move closer to a future where diabetes can be effectively managed or even cured, improving the lives of millions worldwide.
Stem Cell Therapy for Inflammation: How It Works and Its Benefits
Stem cell therapy has revolutionized the approach to treating various inflammatory conditions, offering new hope and possibilities. By harnessing the body’s natural healing mechanisms, this advanced treatment aims to reduce inflammation and improve the quality of life for millions of individuals. One leading provider of this innovative therapy, the Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute, is proudly American-owned and operated. This article delves into the mechanics of stem cell therapy for inflammation, its benefits, and the transformative impact it can have on patients’ lives.
Understanding Inflammation and Its Impact
Inflammation is a biological response triggered by the immune system to protect the body from harmful stimuli such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. While acute inflammation is a crucial part of the healing process, chronic inflammation can lead to a host of debilitating diseases. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 54 million Americans suffer from some form of inflammatory disease. These conditions significantly impact the quality of life and can lead to severe complications if not managed effectively.
Common Inflammatory Diseases
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune disorder characterized by the immune system attacking the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and potential joint destruction. It affects approximately 1.3 million Americans.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): A disease where the immune system attacks the protective sheath (myelin) that covers nerve fibers, resulting in nerve damage and disrupted communication between the brain and the rest of the body. Over 350,000 Americans are diagnosed with MS.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): This includes conditions such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, where chronic inflammation affects the gastrointestinal tract, causing severe digestive issues and abdominal pain.
- Psoriasis: An autoimmune condition that accelerates skin cell production, causing scaling and inflammation of the skin. It affects more than 8 million people in the U.S.
- Lupus: A systemic autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks its tissues and organs, leading to widespread inflammation. Approximately 1.5 million Americans have lupus.
Read Also: Know More About Stem Cell Therapy In Dallas
How Stem Cell Therapy for Inflammation Works
Stem cell therapy, particularly using mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), offers a groundbreaking approach to treating inflammation. MSCs are derived from the umbilical cord (Wharton’s Jelly) and possess unique properties that make them highly effective in managing inflammatory conditions.
Key Mechanisms of MSCs
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: MSCs modulate the immune system by secreting bioactive molecules that reduce inflammation and promote tissue repair. This helps in mitigating the chronic inflammatory response seen in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
- Regenerative Capabilities: MSCs have the potential to differentiate into various cell types, aiding in the repair and regeneration of damaged tissues, which is crucial for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
- Paracrine Effects: MSCs release growth factors and cytokines that stimulate the body’s own repair mechanisms, enhancing the function of affected tissues and promoting overall healing.
- Immunomodulation: MSCs balance the immune response, preventing the immune system from attacking the body’s own tissues. This immunomodulatory effect is particularly beneficial in autoimmune diseases where the immune system is overactive.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy for Inflammation
- Pain Relief and Reduced Inflammation
One of the most significant benefits of stem cell therapy is its ability to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Clinical studies have shown that patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory conditions experience significant improvements in pain levels and joint function after stem cell treatment. For instance, a study published in Stem Cells Translational Medicine reported that 70% of patients with knee osteoarthritis experienced significant pain relief and improved joint function after receiving MSC therapy.
- Enhanced Mobility and Quality of Life
Patients undergoing stem cell therapy often report improved mobility and a better quality of life. For individuals with conditions like multiple sclerosis, stem cell therapy can slow the progression of the disease and enhance neurological function, leading to greater independence and improved daily living.
- Reduced Dependency on Medication
Traditional treatments for inflammatory diseases often involve long-term use of medications, which can have various side effects. Stem cell therapy offers a natural alternative, potentially reducing the need for drugs and minimizing their associated risks. This can be particularly beneficial for patients who experience adverse effects from conventional medications.
- Long-Term Efficacy
Research indicates that stem cell therapy can provide long-lasting relief from inflammation. Unlike conventional treatments that may offer only temporary symptom relief, stem cell therapy addresses the underlying causes of inflammation, promoting sustained healing and recovery. A study conducted by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) found that patients with multiple sclerosis showed reduced disease activity and improved neurological function following stem cell treatment.
Read Also: Exploring the Potential of Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Multiple Sclerosis Treatment
Real-World Impact and Statistics
The effectiveness of stem cell therapy is supported by a growing body of clinical evidence. For example, a study published in the journal Stem Cells Translational Medicine reported that 70% of patients with knee osteoarthritis experienced significant pain relief and improved joint function after receiving MSC therapy. Another study found that patients with multiple sclerosis showed reduced disease activity and improved neurological function following stem cell treatment.
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), over 350,000 Americans are diagnosed with multiple sclerosis, and approximately 1.3 million Americans live with rheumatoid arthritis. For these individuals, stem cell therapy represents a beacon of hope, offering the possibility of managing symptoms and enhancing their quality of life.
Stem Cell Therapy at Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute
Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute utilizes mesenchymal stem cells obtained from the umbilical cord (Wharton’s Jelly). These cells, sourced ethically and safely from newborn umbilical cords, possess potent anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties. The institute’s approach is grounded in rigorous scientific research and clinical expertise, ensuring patients receive the highest quality of care.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy for inflammation represents a transformative advancement in medical science, offering new hope to millions of individuals suffering from chronic inflammatory conditions. By harnessing the power of mesenchymal stem cells, this therapy provides a natural, effective, and long-lasting solution to inflammation and its associated symptoms. As more research and clinical trials continue to validate its efficacy, stem cell therapy stands poised to become a cornerstone of modern medicine, improving lives and fostering better health outcomes.
Stem Cell Therapy Vs. Gene Therapy – Key Comparisons
Stem cell and gene therapy are two rapidly progressing fields in medical research as both have outstanding potential in treating a broad range of chronic diseases. From blood-related disorders, autoimmune conditions, and cardiac problems to genetic disorders, these revolutionary approaches are transforming the treatments of medical conditions.
This blog post begins with an overview of the two types of regenerative medicine: stem cell and gene therapy. Next, we will explore their differences and future in the medical field. Let’s get started!
Table of contents:
What is Gene Therapy and its types?
Gene therapy is an advanced medical treatment that modifies or replaces defective genes with normal genes to treat genetic disorders and prevent them from affecting quality of life. Genes are carriers of information that tell cells to do things, facilitating normal functioning in the human body. Defective genes can not perform this task and make you sick. In such a situation, gene therapy can help. It works by substituting a disease-carrying gene with a healthy gene or deactivating that defective gene.
Gene therapy is an experimental technique that was first successfully done in 1989. It is generally of two types.
- Somatic Gene Therapy – This therapy involves the human body’s somatic cells or stem cells. It is considered the safest and most reliable technique of gene therapy. In this therapy, damaged cells carrying defective genes are replaced with healthy stem cells containing therapeutic genes.
- Germline Gene Therapy – Germline gene therapy inserts healthy DNA into the reproductive cells, i.e., sperm or eggs, to correct the genetic variants. This therapy prevents the disease-causing genes from passing from parents to children and their future generations by altering the genetic material of reproductive cells.
What is stem cell therapy, and what are its types?
Stem cell therapy is a regenerative medicine approach used to treat various diseases. Healthy stem cells are infused into the patient’s body to replace the dysfunctional tissues and promote the healing response of the damaged tissues. Stem cells can differentiate and multiply into specific types of cells for various functions, such as nerve, blood, skin, bone, heart, or muscle cells. These specialized cells are delivered to the injured site to accelerate repair response.
There are four types of stem cells based on the source of collection:
- Adult stem cells – Found in adult humans in specific tissues, such as bone marrow, adipose (fat) tissues, or human umbilical cord tissue.
- Embryonic stem cells – Pluripotent stem cells collected from the inner cell mass of human embryos called blastocysts in their early stages (3-5 days old).
- Induced pluripotent stem cells – Adult stem cells reprogrammed to exhibit properties of pluripotent cells, capable of becoming any cell type.
Read Also: Healing Power Of Stem Cell Therapy: A Comprehensive Guide
Differences between Stem cell therapy and Gene Therapy
At its core, the prime point of difference between gene therapy and stem cell therapy is the mode of attack. The former goes a level deeper in terms of complexity. The primary areas of comparison between the two therapies include:
- Approach – While gene therapy involves transferring genetic materials into the target cells to alter cell functions or correct disease-carrying mutations, cell therapy aims to introduce functional cells into the diseased tissues to replace or repair them.
- Therapeutic factors or agents – Stem cell therapy uses live human cells as its agents. In contrast, gene therapy uses genetic materials, such as DNA or RNA, as therapeutic agents.
- Delivery Method – In stem cell therapy, new healthy stem cells are infused intravenously into the bloodstream to activate the healing process in the affected tissues. Genetic materials are transferred directly to the host cells through complicated techniques, such as viral vectors or repetitive DNA sequences (CRISPR).
- Target Diseases – Stem cell therapy is usually effective in treating age-related problems, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular issues, autoimmune disorders, cancer, and stroke recovery. Gene therapy primarily treats genetic or inherited disorders like sickle cell disease, hemophilia, thalassemia, etc.
- Timeline of benefits – Although both therapies aim to provide long-term and sustainable results, stem cells can offer short-term benefits such as recovery from pain and inflammation in orthopedic injuries.
The Future of Gene and Stem Cell Therapy
Now the question comes: where are cell and gene therapy headed next? Technological advancements will make these treatment approaches personalized and effective, catering to each patient’s unique needs.
Innovations in biotechnology will drive the progress of cell-based therapies in the future, optimizing treatment and stem cell delivery methods. The stem cell field is poised for rapid growth because it is widely adopted for treating a range of medical conditions, from Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease to lung and heart diseases.
Gene therapy, on the other hand, has shown tremendous potential to treat intractable diseases. A new era of personalized gene therapy will emerge as more focus is given to genetic engineering or gene editing technologies, driving innovation and success of medical treatments.
Read Also: Is Stem Cell Therapy A Cure For Neurodegenerative Diseases?
Closing Thoughts
Stem cell and gene therapy are two path-breaking medical science innovations transforming treatments for various medical conditions and genetic disorders. While stem cells target damaged or diseased tissues to support healing and recovery, gene therapy is a functional replacement of cells on the DNA or genetic material level. Several medical companies are pursuing advanced cell or gene therapies to help patients return to everyday and healthy lives.
Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute is a well-known stem cell center in Mexico that provides high-quality, personalized stem cell treatments to patients with various health conditions worldwide. Please speak to our medical experts today to start your stem cell journey with us!
Stem Cells Vs. Progenitor Cells: A Comparative Study
Researchers focus more on various cell groups and their defining properties in stem cell biology. Regenerative medicine with stem cells aims to revolutionize treatments for various severe and chronic diseases. Alongside stem cells, the term “progenitor cells” is also gaining much interest and curiosity in the medical community.
This article will highlight the technical difference between the two cells and how each contributes to treating diseases.
Table of Contents
What are stem cells?
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can develop and multiply into any cell type in the body. The unique ability of stem cells to self-renew and recreate functional tissues has led to its promising applications in cellular therapies.
Stem cells have varying potential for differentiation. For instance, embryonic stem cells and umbilical cord tissue-derived cells are pluripotent, meaning they can differentiate into every cell type. Adult stem cells are multipotent in specific tissues or organs of the human body, such as bone marrow and adipose or fat tissue. Their differentiation potential is limited and specific to their sources of origin.
Read Also: Stem Cell Basics: What They Are And How Do They Work
What are progenitor cells?
Stem cell is a generic or umbrella term referring to all specialized and unspecialized cells capable of self-replicating through cell division. Progenitor cells arise from stem cells and are called their immediate descendants.
Through asymmetric cell divisions, stem cells renew and give rise to tissue-specific cells called progenitors, which differentiate further and multiply into limited numbers.
The primary difference between stem cells and progenitor cells is their differentiation capability. Unlike stem cells, progenitor cells can only differentiate into cells belonging to the same tissue or organ. To put it simply, they are unipotent cells with restricted cell potency. Progenitor cells aim for a final target for cell differentiation and renewal.
Comparison Between Progenitor Cells and Stem Cells
Although progenitor cells are a type of stem cell, they are more specific in their regenerative capability and function. Stem cells have the remarkable potential to differentiate and develop any cell type infinitely and possibly form a whole organ by regenerating tissues. On the contrary, progenitor cells can only grow and self-renew into a specific cell type, thus limiting its applicability in regenerative medicine.
Here is a comprehensive study of both types of cells based on their properties, types, functionalities, and benefits.
Properties of Stem Cells
- Stem cells are unspecialized cells that self-replicate indefinitely through asymmetric cell division.
- All stem cells have multilineage differentiation potential, meaning they can form all types of cells in the body.
- They can repair and regenerate damaged tissues while replenishing dying cells in the diseased area.
Properties of Progenitor Cells
- Progenitor cells are specialized stem cells specific to a particular tissue or organ.
- A progenitor cell can differentiate into its “target cell” and, hence, is unipotent.
- They can divide and self-replicate into a specific cell type a limited number of times.
- Through restricted cell differentiation, progenitor cells can create more progenitor cells or fully matured differentiated cells.
Types of Stem Cells
Stem cells are classified into four main types based on their collection sources.
- Adult stem cells
- Embryonic stem cells
- Fetal or umbilical cord stem cells
- Induced pluripotent stem cells
Types of Progenitor Cells
The undifferentiated stem cells transform into mature cells for blood, tissue, or organ development. During the transformation journey, the immature stem cells undergo cell division to give rise to various types of progenitor cells.
- Neural progenitor cells (cells in the central nervous system)
- Hematopoietic progenitor cells (blood-forming cells)
- Pancreatic progenitor cells
- Endothelial progenitor cells
Benefits of Stem Cells
When stem cells are introduced into the body through stem cell therapy, the new cells reach the diseased area, repair the injured cells, and act on surrounding cells to help the body heal naturally.
- Through tissue regeneration, stem cells can potentially treat neurodegenerative diseases, orthopedic injuries, spinal damage, and cardiac and pulmonary disorders.
- Stem cells have immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties, effectively treating autoimmune diseases like Rheumatoid Arthritis, Lupus, Psoriasis, and Multiple Sclerosis.
- These cells are used in anti-aging treatment as they can regenerate skin cells and delay the process of aging, defying the frailty of aging.
Benefits of Progenitor Cells
Since progenitor cells can form only a single cell type, they can support cellular repair and maintenance in a specific tissue or organ.
- Progenitor cells serve as the body’s repair mechanism by replenishing special cells.
- They are beneficial in ongoing tissue maintenance in the blood, intestinal, nervous systems, and various organs in the body.
- They help faster recovery and tissue healing by replacing damaged or dead cells.
Read Also: Stem Cell Therapy: Ischemic Stroke Recovery Breakthrough
Therapeutic Applications of Stem Cells and Progenitor Cells
Continued research and advancements in regenerative medicine offered hope to patients with chronic and life-threatening conditions. Stem cells repair and regenerate damaged tissues from disease, injury, or aging. Progenitor cells are being explored alongside stem cells for their potential to treat diseases or injuries.
However, more research is needed to understand better how progenitor cells function on a molecular basis. On the contrary, stem cells have progressed from early research and experimental trials to therapeutic use.
Concluding Thoughts
Stem and progenitor cells are emerging medical research topics due to their unique capacity to differentiate and regenerate cells. Stem cells are currently utilized to provide stem cell therapies to treat patients suffering from various diseases via intravenous infusions or bone marrow transplants Cell-based regenerative treatments assist patients in recovering from diseases through tissue repair and healing.
Moreover, researchers are exploring the possibility of utilizing progenitor cells to generate diverse tissues, including blood vessels, heart valves, and organ-specific cells, for ongoing cell repair and maintenance in the body.
Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute is a well-established stem cell center in Mexico, known for its cutting-edge treatments and highly qualified medical professionals. If you want to learn more about stem cell therapy and the conditions we treat, schedule a consultation with our experts today.
Is The Process Of Stem Cell Therapy Painful?
Stem cell therapy has gained much attention and interest in the past few decades as a revolutionary approach to treating severe medical conditions and injuries. This path breaking avenue to disease treatment and symptom management offers promising hope to patients with chronic conditions like autoimmune diseases, neurologic disorders, heart problems, infertility issues, and more.
Stem cells’ distinctive properties are utilized in therapy to regenerate or repair damaged tissue and support natural healing. But one question frequently arises and bothers most patients before getting stem cell treatments: whether the process is painful.
This article will explore stem cell therapy basics and discuss what patients can expect during the treatment.
Understanding The Fundamentals Of Stem Cell Therapy
Before grasping the pain aspects and other details of the treatment process, you must understand stem cell therapy by learning the basics behind this groundbreaking regenerative medicine and how it works.
Stem cells are special undifferentiated cells found in the human body, possessing the distinct capabilities to differentiate and transform into any cell type. Cells can be sourced from various body parts like bone marrow, fat or adipose tissue, hip bone, early-stage embryos, and umbilical cord tissue.
Stem cell therapy involves using cells’ unique properties to promote tissue repair and regeneration, which can be used to treat a range of chronic medical conditions.
Read Also: 7 Common Questions By Patients Before First Stem Cell Therapy
How are stem cells harvested?
Cell-based treatment involves harvesting stem cells from the patient’s body or a donor and injecting them into the diseased area requiring treatment.
The pain level experienced while harvesting stem cells depends on the sources and methods used for collection. So, let’s get a clearer picture of the cell harvesting process.
- Bone Marrow – Stem cell extraction from the bone marrow is a somewhat painful experience because it requires inserting a needle into the pelvic bone to collect the stem cells. Most clinics prefer to avoid using this technique because the process is painful and uncomfortable, and fewer cells can be extracted.
- Adipose or Fat Tissue – A relatively less painful and easy process of stem cell collection and harvesting. Fat cells are obtained from the donor’s or patient’s body through a small liposuction process.
- Umbilical Cord Tissue (UCT) – Mesenchymal stem cells are obtained from umbilical cord tissue from donor sources and don’t cause discomfort during extraction. Following healthy births, the cells are isolated from newborn babies’ umbilical cord tissue (Wharton’s Jelly).
Most stem cell therapy clinics use mesenchymal stem cells of UCTs because they are young cells with high proliferation capacity and multilineage differentiation potential. They can differentiate and develop into any cell type, thus repairing and regenerating tissues in the damaged areas.
Methods of Stem Cell Administration and Pain Associated With Them
Stem cell delivery into the patient’s body can be done through various routes, the most widespread of which is intravenous infusion.
Intravenous delivery
Intravenous infusions are painless, similar to a standard IV procedure. Healthy stem cells are slowly infused into the bloodstream via IV drip. The cells are administered by inserting a thin needle into the blood vein. The method is generally painless and requires one to two hours to complete.
Stem cell injection
In some instances, such as knee pain or shoulder injury, the cells are injected into the affected areas. The pain is mild, as patients might have a slight needle prick or burning sensation at the site of the injection.
Intrathecal (lumbar puncture) procedure
The method allows targeted delivery into the cerebrospinal fluid to reach the central nervous system. Intrathecal administration is mainly used in treating neurodegenerative diseases such as spinal muscular atrophy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, etc. Patients might experience pain at the insertion site, so doctors may use local anesthetics to eliminate pain and discomfort.
It is essential to understand that the pain thresholds of individuals vary. For some, the pain might seem minimal, while others may find the process extremely painful. Hence, every patient must communicate their level of pain tolerance with the medical professionals to ensure adequate pain management measures are implemented during the procedure.
Read Also: Is Stem Cell Therapy A Cure For Neurodegenerative Diseases?
Pain Management Techniques During Stem Cell Treatment
Stem cell therapy centers and healthcare providers understand the pain associated with stem cell therapy and the patient’s concerns. To eliminate pain, doctors might follow any of the pain management strategies below.
- Local Anesthesia – For processes like intrathecal administration involving needle insertion, local anesthetics are used to numb the area so the patient doesn’t feel pain or discomfort.
- Pain-relief Medications – When doctors feel a patient’s pain tolerance is low, they can suggest pain medications before or after the procedure to mitigate the pain.
- Cryotherapy – Cold therapy is also used to provide relief to patients. Applying ice packs on the site of injection helps reduce pain and swelling post-treatment.
Contact Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute For A Safe And Comfortable Experience
At Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute, we prioritize patient’s comfort and safety. Our healthcare professionals aim to give our patients a smooth and painless journey of stem cell therapy. We take necessary pain management measures to mitigate pain and ensure comfort.
As a well-established stem cell center in Mexico, we have made great strides in transforming the lives of thousands with our cutting-edge, high-quality stem cell treatments. Connect with our stem cell specialist, Doctor Josemaria Torres Farber, to learn about the stem cell administration process and determine whether you are an eligible candidate.
Summary
Stem cell therapy has emerged as a novel therapeutic approach that utilizes the body’s natural healing potential to treat chronic diseases. Using stem cells promotes the healing and regeneration of damaged tissues, potentially evading invasive and expensive surgeries and long-term medications.
Cell-based therapy is a rising avenue for medical treatment, offering hope to millions worldwide. But when it comes to pain, most patients get afraid and cannot decide whether to go for the treatment.
I hope this article is successful in explaining the kind of experience you can expect from the treatment. The level of discomfort and pain varies from person to person, depending on the method of administration and the individual’s pain threshold. However, it can be ascertained that the pain is minimal and tolerable. If a patient feels pain, medications are administered to provide comfort.
Contact the best stem cell therapy hospital in Mexico for a painless and comfortable stem cell therapy experience.
Stem Cell Basics: What They Are And How Do They Work
Stem cells are specialized cells that have the potential to develop and multiply into different types of cells. Their unique ability to self-renew and recreate functional cells and tissues serves as a repair mechanism for the human body. They can cure various diseases and give individuals a new lease of life.
This article puts forward the basics of stem cells, what they are, their sources, and how they function in the body to treat a disease. So, let’s begin!
Table of contents:
What are stem cells?
Stem cells are like the building blocks or foundation of the human body from which life starts. These are unspecialized cells capable of differentiating and multiplying repeatedly into more than 200 types of specialized cells to form a human body. They continuously divide and self-renew to become differentiated cells such as blood, muscle, bone, nerve, skin, and organ-specific cells.
Besides differentiating into specialized cells, stem cells can also repair damaged tissues. Right now, reputed stem cell therapy clinics all over the world are utilizing this remarkable property for stem cells to provide stem cell-based therapies to treat serious illnesses such as Autoimmune diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, orthopedic conditions, spinal cord injuries, heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, etc.
Moreover, medical researchers and clinicians are working closely to explore other distinct qualities of stem cells and unveil their therapeutic applications as a possible cure for other diseases.
What are the various types of stem cells?
Scientists and experts classify stem cells by their sources and function into three broad categories.
Embryonic stem cells (Pluripotent)
Stem cells are obtained from early-stage embryos (in the blastocyst stage) or donated umbilical cord tissue. These are pluripotent cells, meaning they have the power to form and divide into any cell type.
Adult stem cells (Multipotent or Unipotent)
Adult stem cells are tissue-specific cells with limited potential to develop into specialized cells. They are mainly collected from bone marrow, adipose or fat tissues, and organs found in the body. They can repair damaged tissues and restore specific bodily functions related to the organ in which they are located. For instance, blood cells isolated from bone marrow can form new blood cells and are used to treat blood-related disorders. They cannot form skin or organ cells; hence, they are called unipotent or multipotent cells.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (IPSCs)
IPSCs are lab-engineered stem cells that resemble the properties of pluripotent cells such as embryonic cells or cord blood stem cells. They are adult stems reprogrammed in a laboratory to function like pluripotent cells and become any cell type. IPSCs have good potential use in regenerative medicine treatment but are still in the research phase.
Why are stem cells important?
Since stem cells are undifferentiated cells capable of dividing and making infinite copies, they hold great promise in treating various medical conditions. They maintain and replenish healthy cells in the diseased areas and function as a repair system.
Researchers are keen on exploring more about stem cells to understand their therapeutic effects in replacing and repairing damaged or unhealthy cells. They are helpful for researchers in understanding how cells grow, change, and develop diseases. They identify and target the root cause of the disease by finding an appropriate treatment solution using stem cells.
Stem cells are also used to replace cancer cells with healthy blood-forming cells for post-cancer recovery. They aid in immuno-reconstitution and eliminate the prolonged side effects that cancer survivors have to go through.
How does stem cell therapy work?
Stem cells have extraordinary power that no other cells possess. They can differentiate into any specialized cells and continuously multiply to create exact replicas of that cell. Normal cells in the human body also renew and divide, but they have limited capabilities and lifespans.
Stem cells have immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties that support the healing of injured or inflamed tissues. They are also known as reparative cells and are put to therapeutic use by doctors and healthcare providers. These cells develop into specialized cells and, on reaching the targeted area, help in tissue repair and regeneration. Given their unique advantages and regenerative abilities, stem cells offer promising hopes for treating a wide range of life-threatening diseases.
Read Also: Effectiveness and Safety Of Stem Cell Therapy For Arthritis
How do stem cell clinics use stem cells to treat diseases?
Stem cells are used in regenerative medicine treatment and therapies because of their self-renewing properties. Leading stem cell therapy clinics rely on mesenchymal stem cells derived from the human umbilical cord tissue (HUCT) for treating chronic conditions. They are the most effective and safe for cell-based therapies because cell rejection by patients is almost zero. HUCT mesenchymal stem cells also eliminate the need for stem cell collection from the patient’s body, which can be an ordeal experience.
Regenerative medicine treatment utilizes the body’s innate healing power and regrows healthy tissue and cells with the help of newly introduced stem cells. As per the opinions of healthcare advocates and doctors, stem cell therapy can be beneficial for treating patients with the following chronic conditions or injuries.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Parkinson’s disease
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Type 1 diabetes
- Heart disease
- Psoriasis
- Lupus
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Orthopedic conditions like knee pain, shoulder pain, back pain, etc.
- Spinal cord injuries
- Lyme disease
- Post-stroke recovery
- Post-cancer recovery
- Muscular Dystrophy
- Anti-aging treatment
- Erectile Dysfunction
Life Altering Stem Cell Therapy Institute is a leading clinic for stem cell therapy in Mexico that uses human umbilical cord tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells to treat debilitating and life-impacting diseases. Their highly qualified doctors, physicians, and stem cell specialists ensure the complete safety of the patients during the treatment. Also, this center’s top-notch facilities and cutting-edge treatment technologies ensure patients have a comfortable stem cell therapy experience.
Conclusion
Stem cells have shown significant therapeutic potential by impacting human health significantly. Over the last few years, the success rate of stem cell treatment has also been high, encouraging scientists and researchers to work more on stem cell biology. New areas of research and treatment applications are yet to be discovered in the upcoming years.
Are you or someone you know suffering from any chronic condition and tired of conventional treatments? Try stem cell therapy! Connect with an esteemed stem cell center in Mexico to give your life a restart and lead a healthier future.